Therefore, the shift of production to the US would take years if not decades of coordinated investments in automation, tools, infrastructure and training. Encouraging foreign component manufacturers to build facilities in the US would also be a challenge.
“If you are a Chinese supplier making a certain type of component that can also be used on a Huawei or Xiaomi phone, you have lever,” Mohan says. “The encouragement to share these factories is low because you are getting staircase and efficiency in China you wouldn’t get if Apple were your only supplier.”
Politics uncertainty is another problem, according to Tsay. “The American system while staying, where everything can be fully roll every four years, it is not favorable for business investments. When people and companies make investments, they must have a longer horizon than that.”
Mark Randall was a senior Vice President in Motorola when he was owned by Google and sought to build her smartphone factory in the US. The idea was not impossible, he says, but “I just knew it would be too difficult.”
The costs of American labor required to turn raw materials into finished goods are “significantly higher” than elsewhere, he says. For example, the US has a shortage of mechanical engineers. For a massive displacement of electronics production in the US, “We are talking about needing tens of thousands of them.”
Tariffs create a “nightmare” when modeling the costs of a new plant, Randall adds. “That is why most companies do not make short -term, strange knee reactions to the type of changes we are seeing today. You have to be super strategic and know where you are going in the long run.”
Done in the US?
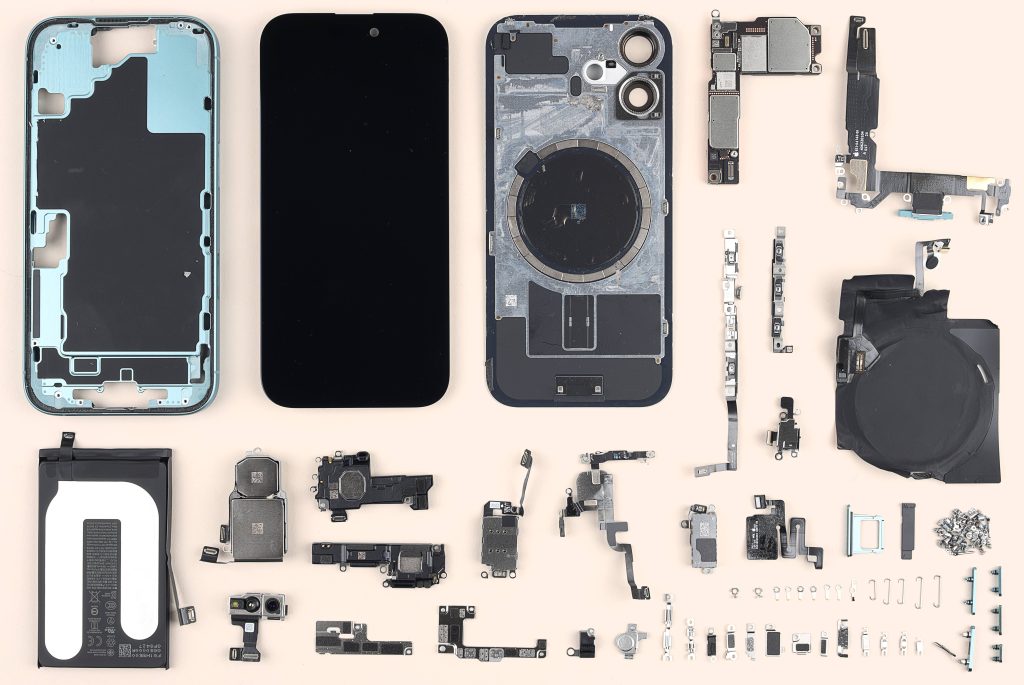
A deeper look THEir feed STRAND ABOUT THREE part WITHIN most recent iPhone pattern illustrates complication BY removable MANUFACTURE BY We, WITHIN A iNduSTRy THAT It requires YEARS BY I DO equal extra shifts.
A component on the currently touch screen in America is the cover, manufactured by Apple Corning’s long glass in Kentucky, though the company also has facilities in China and India.
But the OLED screen that helps maintain battery life and a multi -integrated layer that enables the screen interaction are mainly produced by Samsung in South Korea.
The main electronic parts that make the functional screen are combined with the screen unit in production facilities in China, before this component is transported to a Foxconn factory to combine with the rest of iPhone.
metal frame masterfully grab challenge BY recessive PORCELAIN BY Apple feed STRAND ABOUT LOT models, coating IS CUTTING AND formed BY A block BY aluminum USER high precision computer numerical control (CNC) cars.
Wayne Lam, an analyst at Techinsights, says the process relies on an “army” of these cars, which Apple’s sellers in China have spent years accumulating and which can currently not be reproduced elsewhere. “If Apple were to make the iPhone in the sea, there would ben’t enough CNC cars that they could buy to meet China’s ecosystem scale,” He says.
Lam adds: “This is a specialized skill that is impossible to repeat outside China.”
Equal iPhone simpler component – his miniature screws – are complex. they ARE done BY different mATERIALS dependent IN their role AND I have A number BY Heads: Philips, flat Tri-pithur AND Pentalob, amidst others.
But it is the process in the process that summarizes the challenges that the company will face if the iPhone production would be moved to the SH.BA Apple design, different from many other smartphone brands, does not use glue to attach the frame, and analysts say it is currently more cost-effective for Foxconn to hire people to make the screw.